Diagnostics
The AI platform BIOMETRICA, developed by jung diagnostics and certified as a medical device, analyses radiological data, quantifies the relevant diagnostic parameters and creates a structured radiological report proposal.
BIOMETRICA standardizes the quality of radiological reporting at a high level, independent of the radiologist, and accelerates the reporting process. This saves valuable time of a radiologist.
You want to try out our products?
BIOMETRICA is being continuously expanded. Currently, the following clinical applications are supported:
- assessment of suspected dementia
- assessment of suspected multiple sclerosis (MS)
- MS follow-up assessment
For this purpose, the following diagnostic parameters are quantified, quality-assured and provided as a biomarker report:
- lesion quantification and localization
- disease-related loss of brain volume (atrophy)
Additionally a structured radiological report proposal is delivered.
The technologies for computer-aided quantification were validated in extensive clinical studies and published in high-ranking scientific and clinical journals. An overview of our publications can be found on the page clinical research.
BIOMETRICA reports consist - depending on the clinical application - of information on different biomarkers:
T2 and contrast enhancing T1 lesions
Not only the total number and volume of T2 lesions and the number of contrast-enhancing T1 lesions are reported, but also the localization of the lesions is specified in four categories (juxtacortical, periventricular, deep white matter, infratentorial).
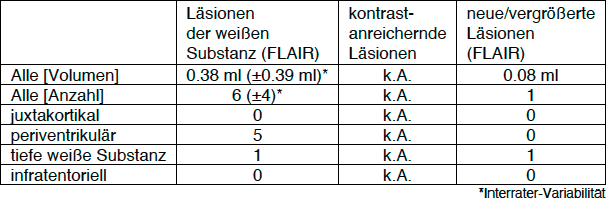
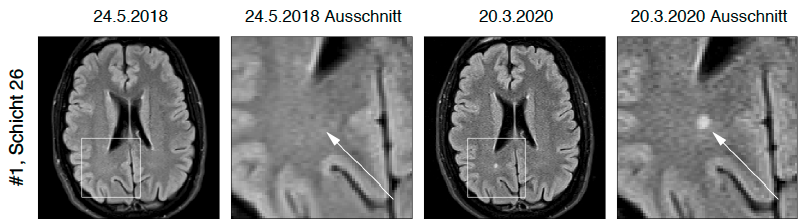
T2 lesion activity (new or enlarged T2 lesions)
If there is a preliminary examination, lesions are also listed which have newly arisen or have developed since the preliminary examination significantly enlarged. The T2 lesion activity is also broken down with respect to localization.
To simplify the assessment, all new/enlarged T2 lesions are shown in direct before/after comparison.
Brain volume loss rate
Once qualified 3D T1 sequences of at least two examinations are available, the brain volume loss rate is calculated. The individual brain volume loss rate is compared against brain volume loss rates of a cohort of healthy subjects in relation to age. The biological variations that are important for a decision are estimated by a confidence interval.
.This enables the reliable differentiation between age-related and disease-related brain volume loss in the individual patient [1][2][3].

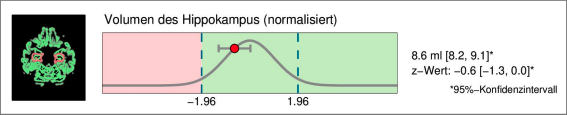
Regional brain volume loss
Especially for the early diagnosis or exclusion of Alzheimer's dementia, the volume of the hippocampus is indicative [4]. Therefore, the hippocampal volume is indicated separately, including comparison with the normative database corrected for age and head size.
.
Focal brain volume loss
To identify focal brain atrophy we use the method of voxel-based morphometry, in which a comparison with a normative database is made for each pixel. This enables a very detailed overview of atrophic brain structures and is therefore particularly suitable for dementia differential diagnosis [5].
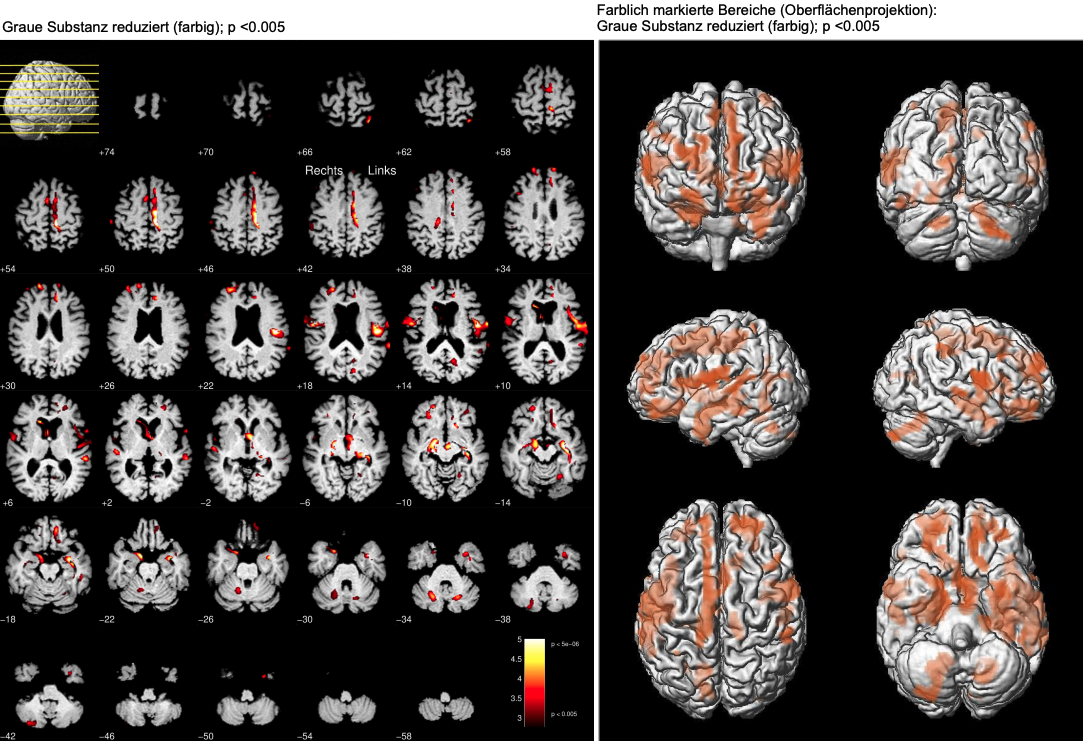
[1] Opfer R, Ostwaldt AC, Sormani MP, Gocke C, Walker-Egger C, Panogaran M, De Stefano N, Schippling S (2018) Estimates of age-dependent cut-offs for pathological brain volume loss using SIENA/FSL – A longitudinal brain volumetry study in healthy adults. Neurobiol. Aging 65:1-6. PubMed
[2] Opfer R, Ostwaldt AC, Walker-Egger C, Panogaran M, Sormani MP, De Stefano N, Schippling S (2018) Within patient fluctuation of brain volume estimates from shortterm repeated MRI measurements using SIENA/FSL. J Neurol. 265:1158-1165. PubMed
[3] Narayanan S, Nakamura K, Fonov VS et al. (2020) Brain volume loss in individuals over time: Source of variance and limits of detectability. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.116737 PubMed
[4] Suppa P, Hampel H, Spies L, Fiebach J, Dubois B und Buchert R (2015) Fully automated atlas-based hippocampal volumetry for clinical routine: validation in subjects with mild cognitive impairment from the ADNI cohort. J Alzheimers Dis. 46:199–209. PubMed
[5] Hedderich DM, Dieckmeyer M, Andrisan T, et al. (2020) Normative brain volume reports may improve differential diagnosis of dementing neurodegenerative diseases in clinical practice. Eur Radiol. 2020;10.1007/s00330-019-06602-0. PubMed

